
As Unified National Networks (UNN) is on the cusp of the final stages of getting the infrastructure ready for the launching of 5G network in Brunei Darussalam this year, it is ideal for the consumers to be updated about what 5G is and what does it means for everyone.
Since 2020 when UNN joined the National 5G Taskforce and made public its position about 5G, it has established proof of concept within a small number of locations around the nation to study the applications of equipment to the network, the needs of the consumers, and how 5G connectivity can be implemented across the country.
These case studies contributed to the establishment of UNN’s national modernization project to expand radio access network (RAN) and upgrade its broadband network to address the increasing traffic and data volume within the country. To date, 90% of the base stations in the country are already modernized and in place with the technology to start 5G services in the country.
So, what is 5G? From our previous article published in April 2022, we detailed the differences between previous generations of mobile networks and 5G, where first generation (1G) delivered analogue voice, second generation (2G) introduced digital voice, third generation (3G) brought mobile data, and fourth generation (4G) ushered in the era of mobile broadband. 5G is the fifth-generation cellular network technology that aims to provide massive bandwidth couple with network capacity, ultra-low latency, better availability, and more reliability.
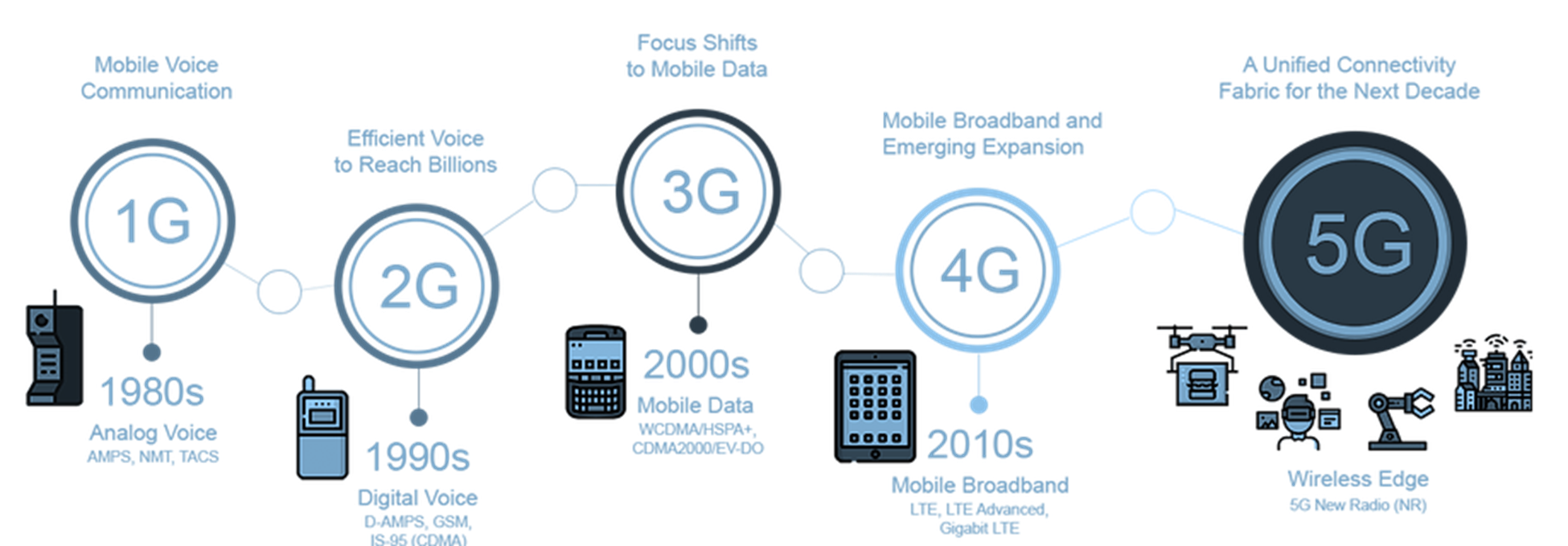
Then, what does this mean for consumers? 5G promises significant speed upgrades, which many consumers translate to faster cell or WIFI services. While it is touted to support download speeds of up to 300 megabits per second (Mbps) compared to 20 to 80 Mbps for 4G, the practicality of 5G is expected to hasten the digital transformation of the country and its people – from healthcare to education to gaming and many other benefits that woudl change the way we go about in our day-to-day lives.
Simply put, the 5G network, if integrated successfully in digital transformation projects, will provide a unified, more capable interface with an extended capacity to enable next-generation user experiences, empower new deployment models and deliver these new services.
Below are some of the exciting things 5G can expect to change business and consumer technology.
Immersive experience. 5G can drive new, immersive Internet of Things (IoT), mobile, home, work, and travel experiences. The low latency of 5G could benefit a wide variety of connected devices such as self-driving car or the emergence of autonomous vehicles, for example, which combines artificial intelligence and IoT to help reduce accidents due to vehicles being interconnected with each other and in constant communication.
5G can also affect the way we make purchases. The current pandemic has seen improvements and growth of online platforms such as Instagram and WhatsApp in Brunei Darussalam to ease the way we buy our food and essential items. With 5G, the IOT will enable the devices and appliances we use every day to make payments, for example, paying for fuel by pressing a button in your car or ordering groceries with your fridge.
Improved and enhanced healthcare. Besides low latency and high capacity, 5G’s potential also comes from its reliability to create efficiencies and bring new products and services to healthcare entities, for example, quick transmission of large imaging files where as soon as patient leaves the X-ray room, the film is already on its way to the doctor.
We have also seen how the pandemic has pushed the clinics in Brunei to carry out consultations online. With 5G technology, the telemedicine market can expect to grow further as the network can support real-time high-quality video to handle telemedicine appointments and real-time monitoring.
Other aspects where healthcare can benefit includes improving of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR), enhancing the doctor’s ability to deliver innovative, less invasive treatments which in turn reduce pain and anxiety for patients by producing calming, distracting content via 5G-enabled AR and VR.
New capabilities for education. The worldwide pandemic has forced students and teachers to log onto platforms such as Zoom, Skype and MS Teams to carry out their studies and lectures. When logging into these platforms, there is propensity to lag and break in connectivity, which impacts their educational delivery.
With 5G, these video conferencing platforms is expected to improve in quality and reliability around the globe while skills such as lab work or hands-on experiences can be integrated into AR and VR for an immersive classroom experience. The revolution of educational environment can increase the flexibility for students and professionals to newer paths of engagement – not just how to use these advanced technologies but also how to develop and create with them.
The very existence of 5G provides a huge opportunity for innovative ideas, new products, and services. And a lot of useful applications are being developed, tested, and implemented around the world for us to refer and adopt to serve us better.
According to the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) 2020 global innovation index edition, Brunei is ranked 71st out of 131 countries on the overall index ranking while achieving the 59th place in the Information and Communication Technologies (ICTs) infrastructure specific thrusts. With all the modernization and investments that UNN is carrying out to the national infrastructure in the past 2-3 years, the ICT ranking improved to 46 in 2021. Brunei could be ranked even higher when 5G network technology is launched this year.
back
